Activity basics
An Activity in ardUI is a single screen you can place widgets on. To create your own Activity, create a new
Activity class as follows: class MyActivity: public Activity {...};. Let's look at this declaration
more closely. A colon in this declaration means that your custom Activity extends a base Activity class.
In other words, it will have all the same fields and methods as any other Activity, while allowing
you to add your own ones. Let's take a look at some of the things an Activity can do for you.
The most important Activity methods are the Lifecycle methods. ardUI will call these
functions at appropriate times for you so that you can do certain things in your application. The only
required method in an Activity is onCreate(). This is the first function called before your
Activity becomes visible. This is also a good place to create and place all widgets your Activity will need.
Here is the chart of the entire Activity lifecycle:
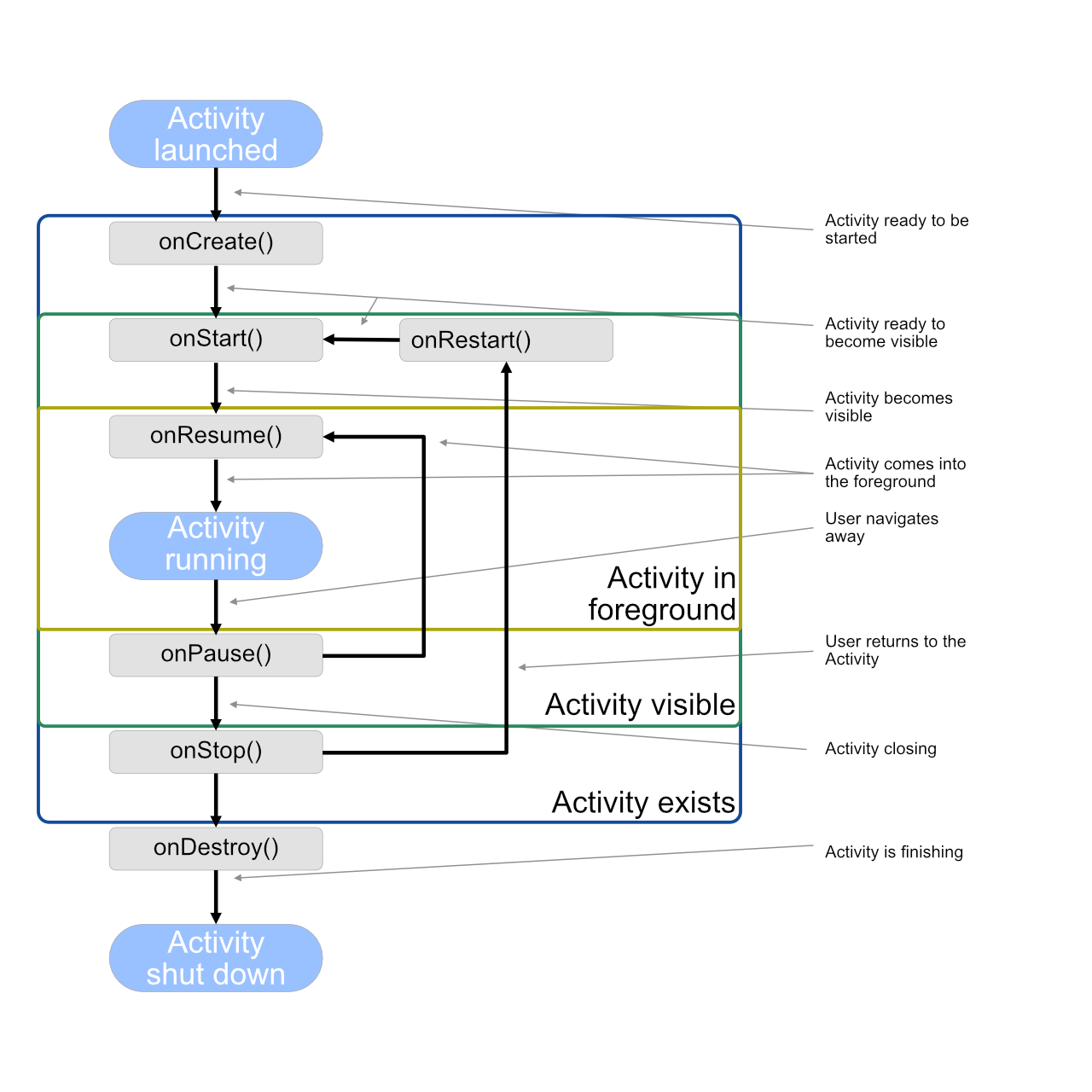
This diagram may look quite complicated at first but you don't have to implement any functions other than
onCreate(). However, you might also want to take a look at the onDestroy() among others.
This is the function ardUI will call before deleting your Activity. This is the last chance for you to release
any resources you are using in your Activity and free all memory you have allocated for it. Otherwise, it might
result in a memory leak. Read more about memory management in ardUI
here.
Switching between Activities
You can open an Activity by calling startActivity() or startActivityForResult(). In both cases,
you may also pass an optional Bundle containing some data you'd like to pass to your new Activity. If you want to
get some data back from it (i.e. input a PIN code on another screen), you should also define a
callback, or a function that will be called once your started Activity finishes. To return a result,
make a call to setResult() from that Activity and, optionally, finish() if you want
that Activity to exit immediately.
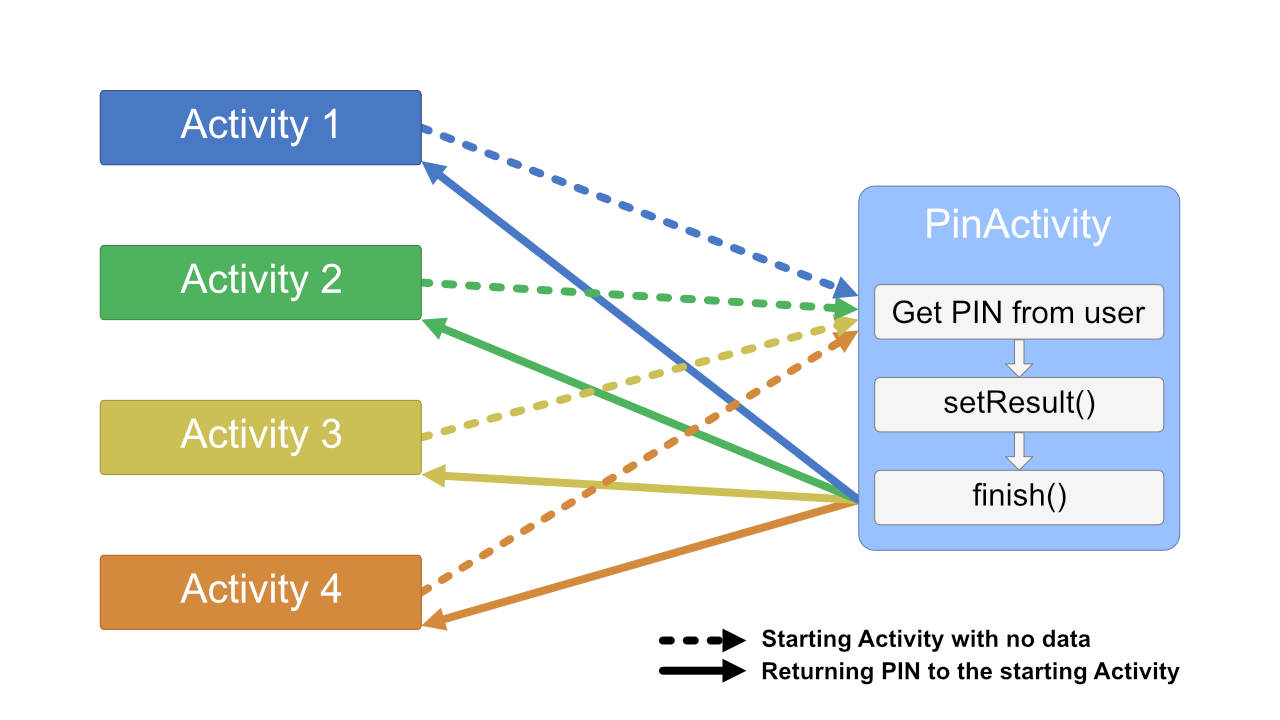
In this example different Activities are starting PinActivity to get a PIN code from the user which is then returned to a result callback. Here is a code example with one main Activity:
#include <Arduino.h>#include "ardUI.h"#include "Activity.h"class PinActivity: public Activity {using Activity::Activity;void onCreate() override {// Obtaining a PIN from the userauto b = Bundle {}; // Creating a new Bundle to return result inb.putInt("pin", /*pin*/); // Adding a pin to a BundlesetResult(0, b); // Setting the Bundle to be a resultfinish(); // Exiting an Activity}}class MainActivity: public Activity {using Activity::Activity;void onCreate() override {// Adding widgets, performing setup, etc.startActivityForResult<ResultActivity>([](int code, Bundle results) -> void {// Bundle "results" now contains our PINSerial.println(results.getInt("pin"));});}}
If you want to stop all Activities immediately and return ardUI to its initial state, just make a call
to the ardUI::reset(). This will stop all Activities currently open and waiting to be reopened and
free all memory taken up by them. You can continue to use ardUI as usual afterwards.
